what causes lactic acidosis in diabetes Causes of lactic acidosis
Lactic acidosis is a medical condition characterized by the accumulation of lactic acid in the body. It occurs when the body produces too much lactic acid or is unable to effectively clear it from the bloodstream. Lactic acid is a normal byproduct of energy metabolism, but when it accumulates at high levels, it can lead to serious health problems. There are several causes of lactic acidosis, and understanding them is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. One of the major causes is tissue hypoxia, which is inadequate oxygen supply to the body’s tissues. During times of oxygen deprivation, such as during intense physical exercise or in certain medical conditions like sepsis or shock, the body starts to rely on anaerobic metabolism for energy production. This produces large amounts of lactic acid as a byproduct, leading to lactic acidosis. Another common cause of lactic acidosis is impaired lactate clearance by the liver. The liver plays a crucial role in metabolizing lactic acid and converting it back to glucose. In conditions like liver dysfunction or liver failure, the liver’s ability to clear lactate from the bloodstream is compromised, leading to lactic acidosis. Certain medications can also contribute to the development of lactic acidosis. For example, metformin, a commonly prescribed medication for type 2 diabetes, may increase the risk of lactic acidosis, especially in individuals with kidney or liver problems. Other medications, such as nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors used in the treatment of HIV, can also cause lactic acidosis. In rare cases, inherited genetic disorders can lead to lactic acidosis. These disorders often affect the enzymes involved in energy metabolism, leading to the accumulation of lactic acid. Examples of such disorders include pyruvate dehydrogenase deficiency and mitochondrial diseases. The symptoms of lactic acidosis can vary depending on the underlying cause and the severity of the condition. Mild cases may present with nonspecific symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and malaise. However, more severe cases can result in profound metabolic disturbances, including electrolyte imbalances, low blood pressure, and organ dysfunction. Diagnosing lactic acidosis involves a combination of clinical evaluation, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. Blood tests can measure the levels of lactic acid in the blood, as well as other parameters that may help identify the underlying cause. Imaging studies, such as ultrasound or CT scans, may be used to evaluate the liver and other affected organs. Treatment of lactic acidosis focuses on addressing the underlying cause and supporting the body’s metabolic processes. In cases of tissue hypoxia, improving oxygen delivery to the tissues is the mainstay of treatment. This may involve supplemental oxygen, intravenous fluids, or in severe cases, interventions to improve blood flow. In cases of impaired lactate clearance, treating the underlying liver dysfunction is essential. This may involve medications to improve liver function, dietary modifications, or in severe cases, liver transplantation. Discontinuing medications that contribute to lactic acidosis is also crucial. Prevention of lactic acidosis involves minimizing the risk factors associated with its development. This includes maintaining proper hydration, avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, and using medications judiciously under medical supervision. In conclusion, lactic acidosis is a medical condition characterized by the accumulation of lactic acid in the body. It can result from various causes, including tissue hypoxia, impaired lactate clearance, medications, and inherited genetic disorders. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of lactic acidosis is important for prompt diagnosis and treatment. By addressing the underlying cause and providing supportive care, healthcare professionals can effectively manage this condition and improve patient outcomes.
If you are looking for Figure 1 from Lactic acidosis: Clinical implications and management you’ve visit to the right page. We have 5 Pics about Figure 1 from Lactic acidosis: Clinical implications and management like Causes of lactic acidosis | Download Table, Difference Between Acidosis and Alkalosis | Definition, Disease and also Difference Between Acidosis and Alkalosis | Definition, Disease. Here it is:
Figure 1 From Lactic Acidosis: Clinical Implications And Management
 www.semanticscholar.orglactic acidosis implications clinical
www.semanticscholar.orglactic acidosis implications clinical
Difference Between Acidosis And Alkalosis | Definition, Disease
 pediaa.comacidosis alkalosis symptoms difference between vs figure
pediaa.comacidosis alkalosis symptoms difference between vs figure
Causes Of Lactic Acidosis | Download Table
 www.researchgate.netacidosis lactic causes
www.researchgate.netacidosis lactic causes
Table 2 From Lactic Acidosis In A Patient With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
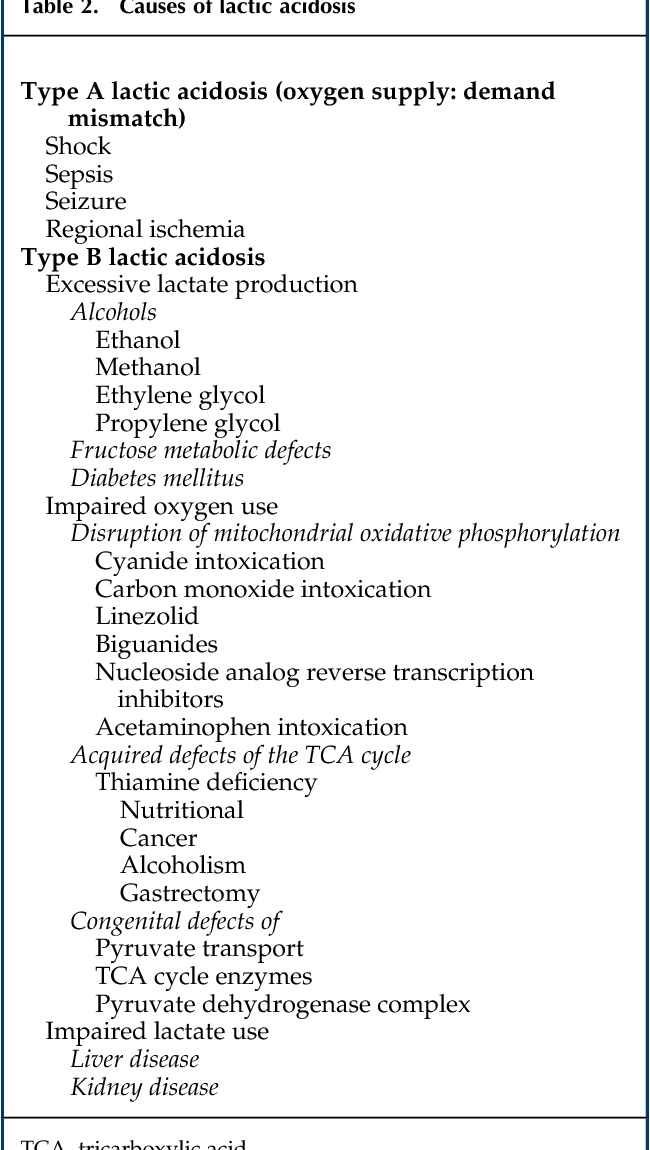 www.semanticscholar.orgacidosis lactic diabetes mellitus
www.semanticscholar.orgacidosis lactic diabetes mellitus
-1 Causes Of Lactic Acidosis | Download Table
 www.researchgate.netacidosis lactic causes
www.researchgate.netacidosis lactic causes
Acidosis lactic diabetes mellitus. Causes of lactic acidosis. Acidosis lactic causes